MP3 has become a cornerstone of the digital audio landscape. It transforms the way we consume and share music. But what is MP3? In this informative guidepost, we delve into the intricacies of MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3. We will explore its origins, its impact on the music industry, and the technology behind its widespread use. Beyond just unraveling the acronym, we’ll navigate through its pros and cons. Also, we will tackle its bitrate and ways to handle it. You will also learn how to play and convert these files efficiently. Additionally, we’ll draw comparisons between MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 and other audio formats. Continue reading for additional insights!


Before we delve into the specifics, let us first answer: What is MP3? Short for MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3, it is a widely used digital audio format. It uses a compression technique to reduce the size of audio data while preserving most of its original quality. This format became a game-changer in the music industry. It addresses the challenge of large file sizes associated with early digital audio.
Furthermore, the compression technique used eliminates certain elements of the audio. These are considered less perceptible to the human ear. It resulted in a significantly smaller file size compared to uncompressed formats. This breakthrough allowed for more efficient storage of music on digital devices. In simple words, it enables the creation, distribution, and consumption of music in a compressed yet accessible form.
Below is the timeline table of the evolution of MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 format. It spans several years, with key milestones occurring in the late 1980s - 2000s. Here’s a timeline highlighting some crucial moments:
| The MP3 Evolution | |
|---|---|
| Year | History |
| 1987-1991 | The development of the MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 format begins. The Fraunhofer Society worked on the compression technique that would later become MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3. |
| 1993 | The first version of the MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 codec is released. It marks the beginning of the practical application of MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 technology. |
| 1995-1997 | The popularity of the format starts to grow as software/hardware support for the format increases. Winamp, one of the early MP3 players, was released in 1997. |
| Late 1990s | The internet facilitates the sharing of this format. It led to the rise of peer-to-peer file-sharing services. This era also sees the establishment of the format as a standard for digital audio. |
| 1999 | The RIAA sues Napster, a popular file-sharing service. It marked the beginning of legal challenges related to copyright infringement and digital music distribution. |
| The Early 2000s | Despite legal battles, the format continues to gain popularity. Portable players, such as the iPod, have become iconic devices. |
| 2007 | The format is officially standardized as ISO/IEC 11172-3 and ISO/IEC 13818-3. |
| 2017 | The Fraunhofer Institute announced that it will no longer enforce its patents, essentially making the format a more freely accessible format. |
MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 has revolutionized the way people store, share, and consume music. It allows for efficient compression of audio files while maintaining a reasonable sound quality. This compression made it practical to store and transfer large amounts of music data.

MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 PROS:
MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 CONS:

After learning what MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 format is, let us now understand what MP3 bitrate is. Briefly, it refers to the amount of data used to represent audio in the format. It is usually measured in kilobits per second (kbps). A higher bitrate results in better quality but also leads to larger file sizes. When comparing bitrates, the two common options are MP3 320 and MP3 V0.

Bitrate: 320 kbps.
320 is a constant bitrate encoding. It uses a fixed amount of data per second to represent the audio. It provides higher audio quality compared to lower bitrates but results in larger file sizes. It’s often considered near-CD quality. Also, it is widely used for music distribution when file size is less of a concern.
Bitrate: Variable, but roughly equivalent to an average of 245 kbps.
V0 is a variable bitrate setting that adjusts the bitrate based on the audio. During simpler parts of a song, it uses a lower bitrate. Meanwhile, it uses a higher bitrate during more complex parts. Despite the variable nature, it maintains high-quality audio while achieving smaller file sizes. It’s a popular compromise between high quality and reasonable file size.

• Understand Bitrate: Bitrate is the amount of data used to represent audio per unit of time. Higher audio bitrate results in better quality but larger file sizes. But you can change the MP3 bitrate with some tools.
To play an MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 file, you can use various players. One of the best players for MP3 is AnyMP4 Blu-ray Player. Though it is designed primarily for Blu-ray discs, it is not limited to Blu-ray content alone. It excels in playing various audio files, including MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 files. It provides a straightforward interface that lets you load and play your favorite tracks. AnyMP4 Blu-ray Player ensures high-quality sound reproduction with crystal clear audio during playback. It allows users to enjoy a premium audio experience.
1. First, Free Download MP3 Player on your computer. Launch the AnyMP4 Blu-ray Player after completing the installation process.
Secure Download
Secure Download
2. Select Open File within the player’s interface. Browse and locate the MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 file you want to play.
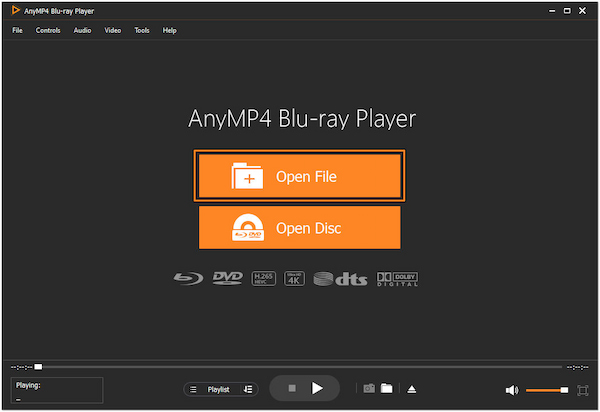
3. AnyMP4 Blu-ray Player will automatically play the loaded MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 file. Use the playback controls to Play, Stop, Pause, Backward, Forward, Previous, and Next.
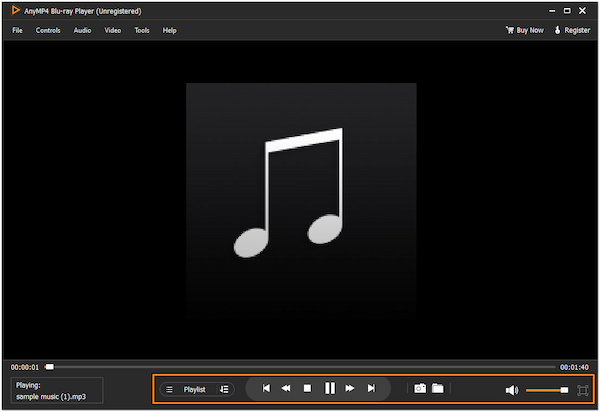
AnyMP4 Blu-ray Player is a dedicated multimedia player you can use as an MP3 player. It provides a convenient solution for users seeking versatile media players that can handle various files. Explore the additional features of AnyMP4 Blu-ray Player by getting a free download now.
Converting MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 files requires an MP3 Converter. AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate is a comprehensive conversion software that goes beyond its name. It offers wide support for audio formats, including MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 files. With this powerful tool, converting to or from MP3 is a seamless process. It supports MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 files both as an input and output format. The best part? This conversion software can transform media files to over 500 file types, including MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3, OGG, M4B, AAC, FLAC, etc.
1. Start by getting a Free Download of AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate. Install it on your computer and complete the installation process.
Secure Download
Secure Download
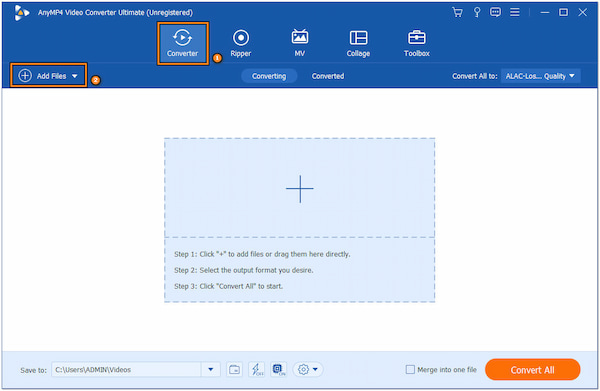
2. Once installed, launch AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate. Within the interface, head to the Converter tab. Click + Add Files to load the media files you want to convert to MP3.
3. Navigate to the Convert All To menu and choose MP3 | High Quality. This option is located in the Audio category.
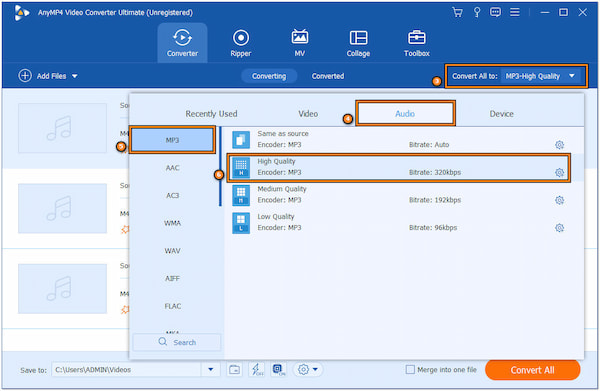
4. In the main interface, click Convert All to start the file conversion process. The software will convert your loaded media files to MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 format.
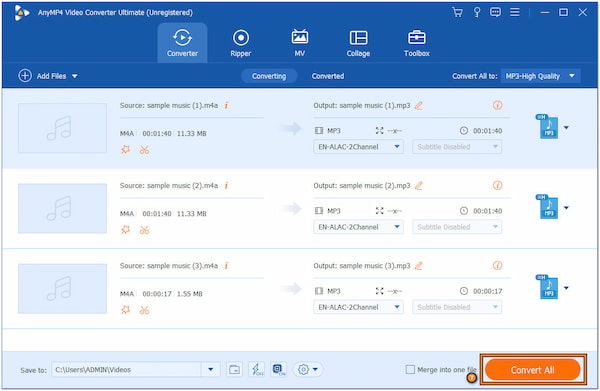
AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate is a flexible MP3 Converter. It allows you to import MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 as an input or output. For good measure, it supports batch conversion. It lets users convert multiple files simultaneously.
This section will provide tips on how to download MP3 files without copyright. Downloading audio files without copyright infringement requires careful consideration of the source and usage rights. That includes Royalty-Free Music, Creative Commons Licensed Music, Public Domain Music, Free Music Blogs, and YouTube Audio Library.

MP3, OGG, and M4B are three different audio file formats. Each of these formats has its characteristics and applications. Understanding their differences is necessary for choosing the most suitable format based on your needs. Check their distinctions below:

It is a widely adopted digital audio format known for its efficient compression. It enables the storage of music with a reasonable file size and audio quality. It has become a standard for general music playback across various devices. It has broad compatibility and support in various software and hardware.

OGG is an open-source and flexible audio format. It supports both lossy and lossless compression. It is often used for multimedia applications and provides similar audio quality to MP3. But, it has a more versatile container. OGG files can contain both audio and metadata. This makes it suitable for several multimedia applications beyond music.
If you need, learn it here to convert OGG to MP3, or MP3 to OGG.

M4B is a format specifically designed for audiobooks. It is particularly associated with Apple’s iOS devices. It can support both lossy and lossless compression. M4B is commonly used with lossy compression to balance audio quality and file size. These files offer unique features tailored for audiobooks, including support for chapter markers and bookmarking. You can convert M4B to MP3 for easy playback.
The table below provides a quick overview of MP3, OGG, and M4B formats. The choice among these formats depends on the use cases. That includes intended use, desired features, and device compatibility. Here are some of their key characteristics:
|
MP3 |
OGG |
M4B |
|---|---|---|
| Fraunhofer Society | Xiph.Org Foundation | Apple Inc. |
| MPEG Audio Layer 3 | Ogg Vorbis | MPEG-4 Book |
| .mp3 | .ogg | .m4b |
| Variable: Depends on the Bitrate | Variable: Depends on Compression Quality | Variable: Depends on the Bitrate |
| Good to Excellent | Good to Excellent | Good to Excellent |
| Lossy | Lossy | Lossy |
| No | Yes | No |
| Yes (ID3 Tags) | Yes (Vorbis Comments) | Yes (iTunes metadata, chapters for M4B) |
| Music, Audio Files | Music, Audio Files | Audiobooks, Podcasts |
| Widely supported | Good support, especially in open-source | Apple devices, iTunes, |
How do I make an MP3 file?
It would help if you had an audio encoding software or converter to create an MP3 file. Choose a tool like AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate. Launch the software, import the audio, and select MP3 as your output format. Adjust settings like bitrate for quality, if available.
Can I send an MP3 file via email?
YES! You can send an MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 file via email. Most email services allow attachments. Simply compose an email, attach the file, and send it. Note that certain email providers may have size limits for attachments. If your file is large, consider compressing the file before sending it.
How do I make an audio file?
You can use AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate to create an audio file. Open the software and import an existing audio file. Export the file in a preferred audio format such as MP3, Ogg, M4B, ACC, FLAC, etc.
The question What is MP3 has now been answered! MP3 has remained a steadfast companion. It delivers a balanced file size and sound quality. If you’re seeking a media player dedicated to playing these files, AnyMP4 Blu-ray Player offers a surprising solution. Despite its Blu-ray-centric name, this player extends its capabilities to support various audio formats. It provides crystal clear sound for high-quality audio files.
Moreover, when the need arises to convert to or from MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3, AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate stands out as a go-to choice. With support for over 500 media formats, it provides a complete solution for all your digital conversion needs. Whether looking for a player to enjoy your collection or a converter to handle various file formats, AnyMP4 Blu-ray Player and AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate stand ready as reliable choices in the realm of digital media.