What is Metadata? You may be familiar with this term or have heard it before. Have you ever thought about what exactly this means? Why is this data needed? To give you a brief background, Metadata is often described as data about data. Simply put, Metadata is particularly important in a file, document, or web page. Another way to explain Metadata is a summary of what the data is.
We can define Metadata in various ways, which we will further explain in this article. Apart from that, we will also present some of the programs you can use to manage the Metadata information of your files, so if you want to learn more about Metadata and how it works. Therefore, we will walk you through this guide.

A set of data called Metadata is used to define other data. Metadata contextualizes other data by giving information like the date and how it was collected, making it simpler to find, access, manage, etc. In other words, obscure data comes with every audio, photo, video, or file. It helps you organize and manage data sets.
There are three main types of metadata: administrative, descriptive, and structural.
Administrative Metadata
With Administrative Metadata, users can find out what kind of instructions, policies, and restrictions have been set on a file. Administrators can restrict file access depending on user qualifications with the help of this kind of data. Administrative Metadata is complete, providing details on specific data from beginning to end. Users now have the opportunity to manage a range of data files.
A simple version of a piece of data is similar to Administrative Metadata. Regardless of how complicated a given data collection may be, its Metadata will be far more comprehensive. Hence, controlling these complicated parts and reducing them for clarity is what Administrative Metadata is all about.
Descriptive Metadata
In its simplest form, Descriptive Metadata is an identifier of certain data. Often, it refers to things like titles, dates, and keywords. For instance, when a user downloads a video file, Descriptive Metadata would include the movie's runtime.
Since that descriptive information is readily available, visible, and pertinent in common file formats, it is frequently used and cited metadata.
It offers basic details about things, such as book titles, authors, dates, and other information, and is one of the simpler sorts of Metadata to comprehend. Descriptive information grows more refined or complicated when utilized to identify distinctive aspects, such as code-driven projects and websites.
Structural Metadata
Structured Metadata provides details about a particular object or resource. It frequently refers to digital media. For instance, a DVD movie contains several different portions. Each segment has a certain running duration for the film, and they all slot together into the structure in a particular order.
In other words, structural Metadata keeps track of information about possible sorting options for a given item or resource. With structural Metadata, users would be made aware of the proper location of these parts on the DVD, as mentioned earlier.
Here are some of the Metadata; check the example given below.
Audio
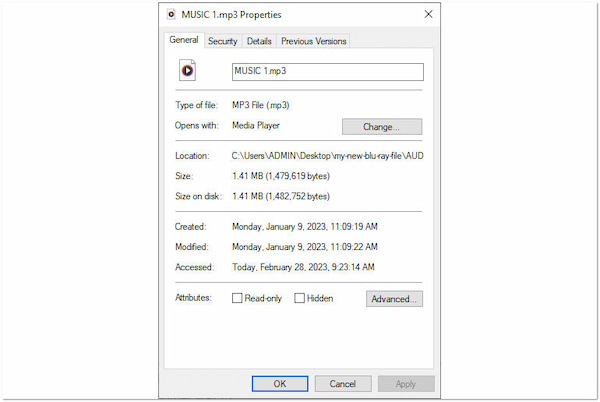
Audio is encoded with data that defines the content and representation of the audio entities.
Pictures

Every photograph we take includes digital Metadata and saves with it.
Videos
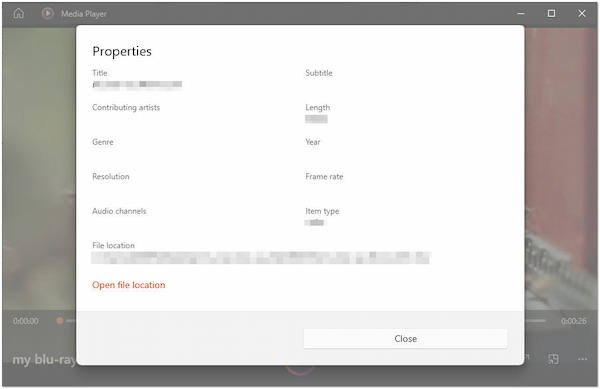
Every time we record videos on our camcorders and digital cameras, the Metadata is attached to the exported video file.
Blog Post

Any blog post has Metadata fields you can often see before the first paragraph.
Books

Each book contains various Metadata on its cover and content.
Desktop Files
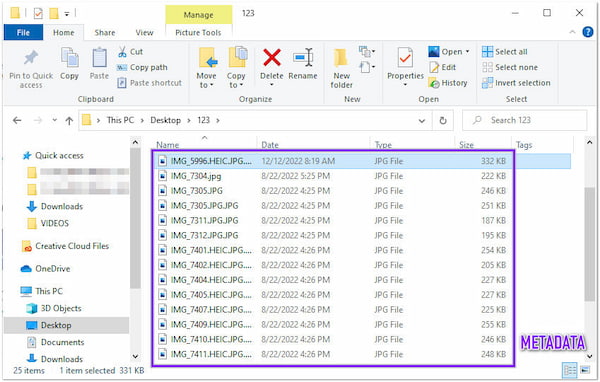
All the information you see in every file from File Explorer is Metadata. The actual data is inside these files.
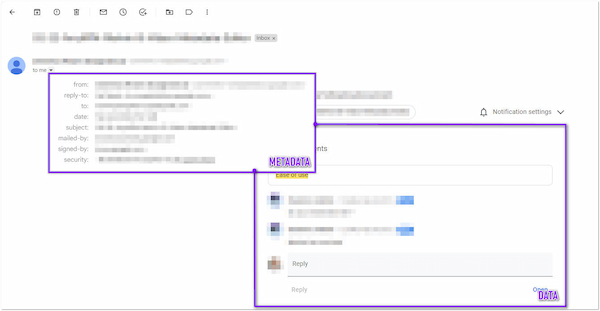
Did you know that every email we send or receive consists of several Metadata? Most of these are hidden and invisible; you can find them in the message header.
Spreadsheets
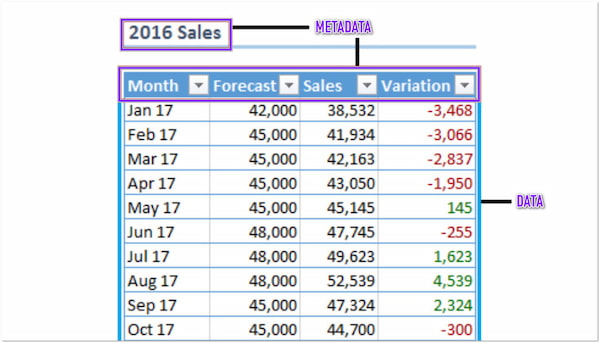
Besides Word documents, Spreadsheets also contain some Metadata.
Web Page
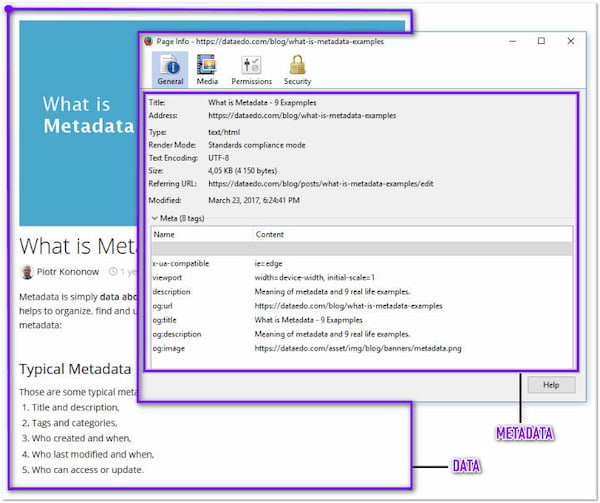
Each web page has a various Metadata
Word Docs
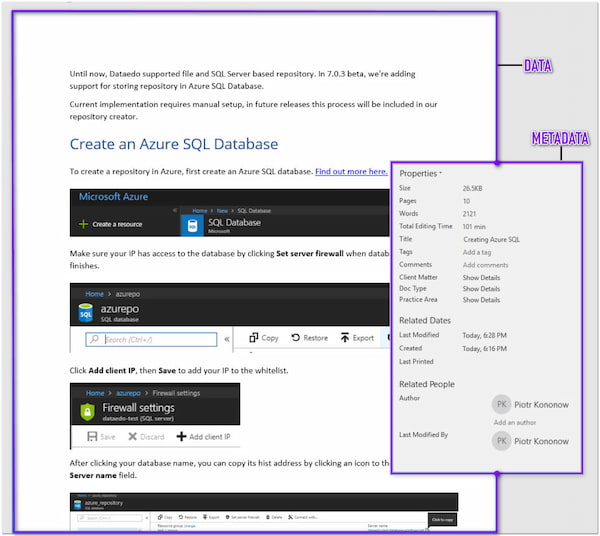
Without exception, each word processing program accumulates Metadata and allows you to add fields for every document you make.
Digital photographs are always stored with a variety of information that is integrated into the image itself. Now, we will define the difference between Metadata and EXIF data.
Digital information that describes the image itself is called Metadata and is kept with each image. It includes important features that explain the image and potential uses in terms that both people and technology can comprehend.
A RAW, JPEG, TIFF, or DNG file might contain Metadata inside or externally as data separate from the original picture.
Three types of Metadata:
Exchangeable Image File Format, or EXIF, refers to the actual Metadata your camera creates and saves each time you take a picture.
Your photographs have data that are incorporated in them, including details about:
|
Editable Info |
Platform |
Price |
Supported formats |
Metadata Editor For |
Best for |
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| File name, title, artist, album, compressor, genre, year, track, comments, and photo thumbnail | Windows, Mac | Starts at $29.96 with a free trial | MP4, AVI, M4A, WAV, M4R, WMV, M4B, ASF, M4P, MP3, 3G2, MOV, M4V, etc. | Video, audio, and thumbnail photo | Beginner, Intermediate, and Professional | Aside from being a Metadata Editor, it also functions as a video/audio solution. | It requires a download before utilizing it. |
| Title, artist, album, date, genre, etc. | Windows, Mac, Linux | FREE | MPEG, AVI, MP4, WMV, WMA, etc. | Video, audio | Intermediate | It is compatible with nearly all platforms | Limited editable info |
| Artist, album, artist, composer, grouping, etc. | Windows, Mac (Old version) | FREE | MP3, WAV, M4V, AIFF, AAC, etc. | Video, audio | Intermediate, Professional | It free to download on Windows and pre-built on macOS (Older versions) | It does not support a newer version of the Mac |
| Artist, track title, track number, album, year, etc. | Windows, Mac | FREE | MP3, WAV, AIFF, AU, OGG, etc. | Audio | Professional | It is a free, open-source, and a multi-platform program | Too complicated interface |
| File name, folder path, profile, target, video profile, etc. | Windows, Mac, Linux | FREE | WebM, AVCHD, HEVC, MP3, AAC, etc. | Video, audio | Professional | It has an intuitive interface | It lacks advanced features |
| Image ID, dimensions, width, height, horizontal resolution, etc. | Windows | FREE | MP4, TIFF, VOB, MPEG, MP3. etc. | Video, audio | Beginner, Intermediate | It is pre-built in all versions of Windows | It doesn't support other OS |
| File name, directory, size, modified date/time, access date/time, etc. | Windows, Mac, Unix | FREE | EXIF, GPS, IPTC, XMP, JFIF, etc. | Photo | Professional | It can modify video Metadata using codes | It only works for coding |
| Title, director, copyright, product, genre, etc. | Windows | FREE | AVI only | Video | Intermediate | It supports multi-tags | It only supports single format |
| Title, actors, directors, artist, copyright, etc. | Mac | Starts at $9.99 | MP4, M4V, and MOV only | Video | Professional | It is a professional Metadata editor for Mac | It's challenging to handle for first time user |
| Title, artist, album, track number, genre, etc. | Windows, Mac, Linux | Starts at $49 (Full-featured) | MP4, MP3, M4P, FLAC, WMA, and OggVorbis only | Video, audio | Professional | It has auto-tagging functionality | It's interface is confusing |
This section will show you how to edit Metadata Info for videos and audio files using AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate.
AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate is a rich-featured program that offers many functions and features, including the Media Metadata Editor tool. Without any prior knowledge of handling the program, you can easily edit Metadata info as it is straightforward and has a neat interface. Below are the guides on how to perform the Metadata info editing.
1. On your computer, download the AnyMP4 Video Converter Ultimate. You can click the Free download button below to possess the program. Complete the installation process and launch it afterward.
Secure Download
Secure Download
2. Next, choose Toolbox from the top menu and select the Media Metadata Editor tool.
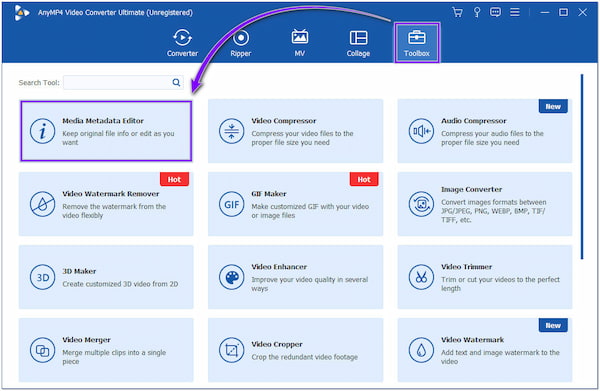
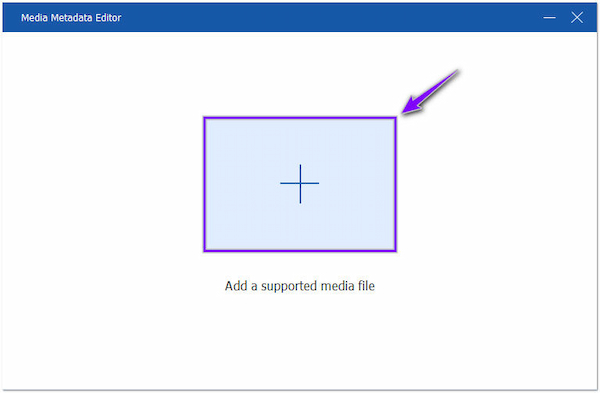
3. After selecting it, a new dialogue will be displayed on your screen. In that case, click the + sign icon to import the video you want to edit Metadata info.
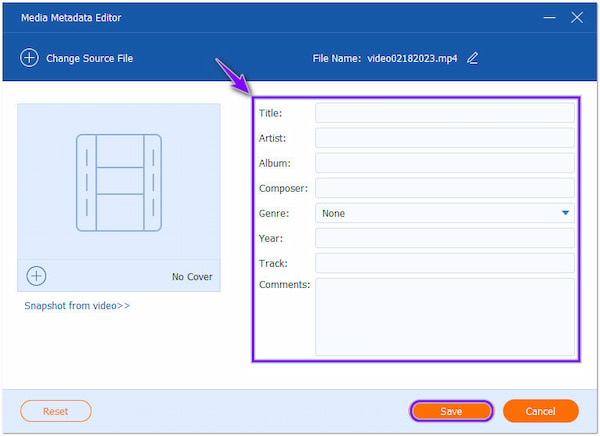
4. Following, determine which data you wish to edit, click each field, and input the desired information. After successfully updating the fields, click the Save button to finish.
The process of editing the Metadata info of the audio file is similar to the above guide. You can also change the file name, title, artist, album, composer, etc.
1. What is an ID3 tag?
ID3 tag is an example of a Metadata container that stores data in a media file. The ID3 tags may contain the following:
• The genre.
• The cover art.
• The album title.
• The artist's name.
• The recording year.
• Other information.
To edit the audio ID3 tag, you will need the music ID3 tag editor.
2. In what ways are Metadata and data different?
Metadata specifies information about the original data, which assists in identifying the type and features of that data. In contrast, data might be a piece of information, a collection of measurements or observations, a story, or a description of a given thing.
3. Is sharing Metadata information safe?
Metadata is a potent idea and usually harmless, yet some contexts may contain sensitive information and confidentiality. Therefore, you should choose the person you share your Metadata information with.
What is Metadata used for? Most Metadata types aid us in making sense of our files and data by providing valuable information. However, it may cause your identity to be at risk once shared with strangers. Yet you don't have to worry; you can modify your Metadata information before sharing it. You can refer to the provided steps above.